1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
|
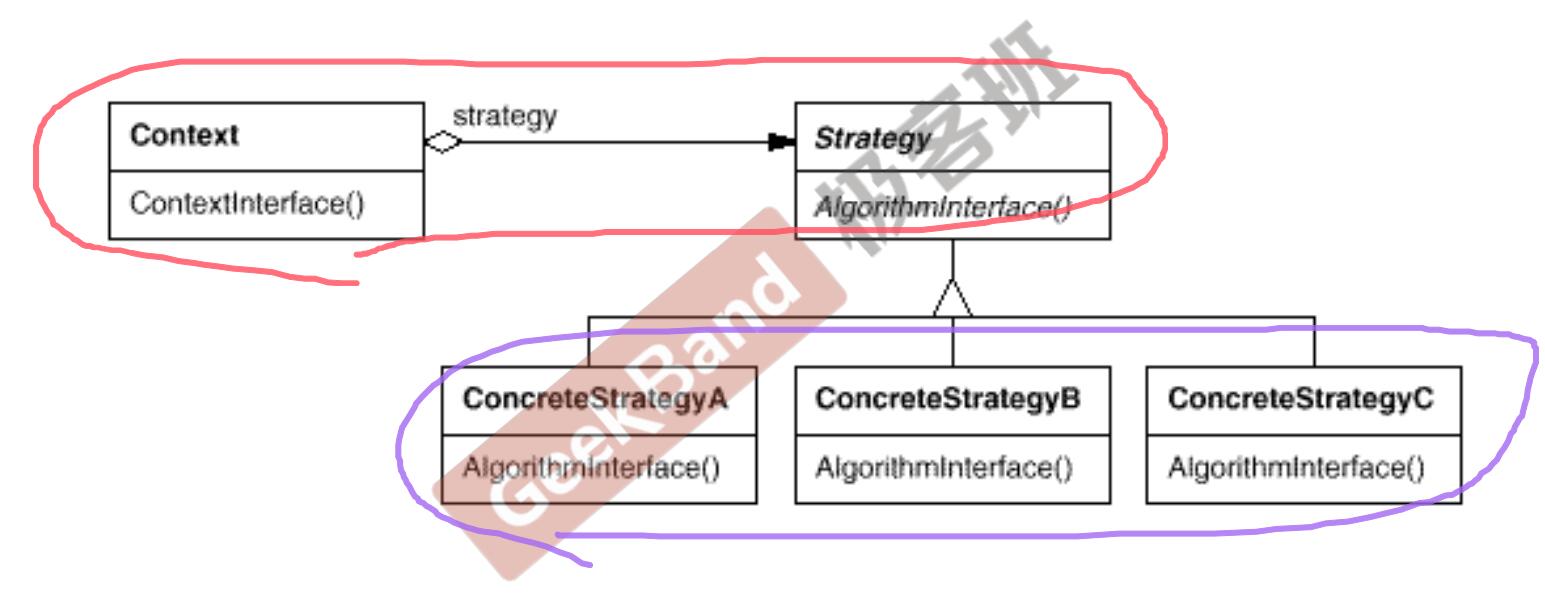
class Strategy {
public:
virtual ~Strategy() = default;
virtual std::string doAlgorithm(const std::string& data) const = 0;
};
class Context {
private:
std::unique_ptr<Strategy> strategy_;
public:
explicit Context(std::unique_ptr<Strategy> &&strategy = {}) : strategy_(std::move(strategy)) {}
void set_strategy(std::unique_ptr<Strategy> &&strategy) {
strategy_ = std::move(strategy);
}
void doSomeBusinessLogic() const {
if (strategy_) {
std::cout << "Context: Sorting data using the strategy (not sure how it'll do it)\n";
std::string result = strategy_->doAlgorithm("aecbd");
std::cout << result << "\n";
}
else {
std::cout << "Context: Strategy isn't set\n";
}
}
};
class ConcreteStrategyA : public Strategy {
public:
std::string doAlgorithm(const std::string& data) const override {
std::string result(data);
std::sort(std::begin(result), std::end(result));
return result;
}
};
class ConcreteStrategyB : public Strategy {
std::string doAlgorithm(const std::string& data) const override {
std::string result(data);
std::sort(std::begin(result), std::end(result), std::greater<>());
return result;
}
};
void clientCode() {
Context context(std::make_unique<ConcreteStrategyA>());
std::cout << "Client: Strategy is set to normal sorting.\n";
context.doSomeBusinessLogic();
std::cout << "\n";
std::cout << "Client: Strategy is set to reverse sorting.\n";
context.set_strategy(std::make_unique<ConcreteStrategyB>());
context.doSomeBusinessLogic();
}
int main() {
clientCode();
return 0;
}
|