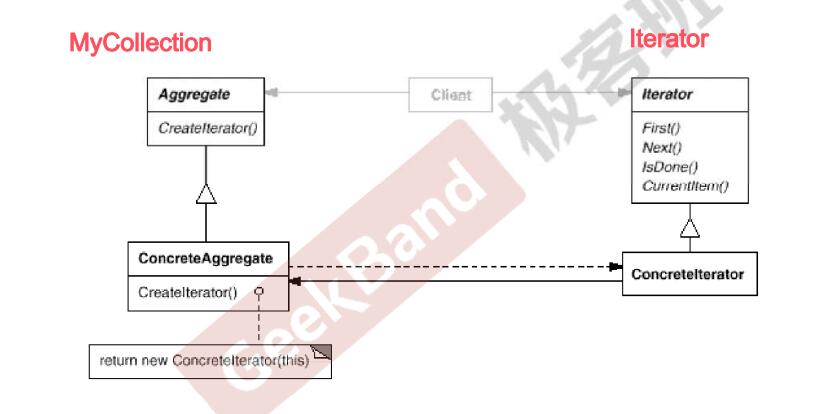
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
|
template <typename T, typename U>
class Iterator {
public:
typedef typename std::vector<T>::iterator iter_type;
Iterator(U *p_data) : m_p_data_(p_data) {
m_it_ = m_p_data_->m_data_.begin();
}
void First() {
m_it_ = m_p_data_->m_data_.begin();
}
void Next() {
m_it_++;
}
bool IsDone() {
return (m_it_ == m_p_data_->m_data_.end());
}
iter_type Current() {
return m_it_;
}
private:
U *m_p_data_;
iter_type m_it_;
};
template <class T>
class Container {
friend class Iterator<T, Container>;
public:
void Add(T a) {
m_data_.push_back(a);
}
Iterator<T, Container> *CreateIterator() {
return new Iterator<T, Container>(this);
}
private:
std::vector<T> m_data_;
};
class Data {
public:
Data(int a = 0) : m_data_(a) {}
void set_data(int a) {
m_data_ = a;
}
int data() {
return m_data_;
}
private:
int m_data_;
};
void ClientCode() {
std::cout << "__________Iterator with int__________" << std::endl;
Container<int> cont;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cont.Add(i);
}
Iterator<int, Container<int>> *it = cont.CreateIterator();
for (it->First(); !it->IsDone(); it->Next()) {
std::cout << *it->Current() << std::endl;
}
Container<Data> cont2;
Data a(100), b(1000), c(10000);
cont2.Add(a);
cont2.Add(b);
cont2.Add(c);
std::cout << "__________Iterator with custom Class__________" << std::endl;
Iterator<Data, Container<Data>> *it2 = cont2.CreateIterator();
for (it2->First(); !it2->IsDone(); it2->Next()) {
std::cout << it2->Current()->data() << std::endl;
}
delete it;
delete it2;
}
int main() {
ClientCode();
return 0;
}
|